As practice has shown, simple level converter with -12V supply derived from DTR/RTS is not capable to work on high speed. Therefore I have made several tests on speed with the original PNP-based design and a RS232 line driver SN75150 and publish test results in this post. Test summary is given in Table 1.
Overview
Experiments were made with four RS232 Level Converter designs:
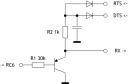
- PNP Transistor, parasitic -12V
- PNP Transistor + JFET current source, parasitic -12V
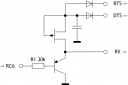
- PNP Transistor, external -5V supply
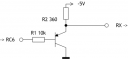
- SN75150 – Dual RS232 Line Driver
Test environment:
- TTL output generated by SISAM in diagnostic mode
- Converter loaded with 1.5m shielded cable (C?‰?100-300pF) + PC USART (Winbond)
Data verification methods:
- watching and reporting framing error condition and
- comparing received data to expected
Test tools:
- SITEST ??“ sends commands to SISAM and forwards data to stdout
- LOOFI ??“ reads data from stdin and verifies the stream against the master pattern, made of the first count characters.
Command lines for tests are the following
SITEST /port=COM1 /count=640000 U03; > c:tempU03.txt
LOOFI /count=224 /file=c:tempU03.txt
SITEST sends U03 command to SISAM. This command turns SISAM in diagnostic mode and SISAM sends sequences of characters 0x20 to 0xFF using baudrate, specified in the command (U00 ??“ 115.2K, U03 ??“ 921.6K). SITEST saves data to file and aborts execution if a framing error is detected. Then LOOFI is used to verify data.
| Test | Max baud rate |
|---|---|
| Hardware loop | 460.8K |
| PNP parasitic -12V | 230.4K |
| PNP parasitic -12V, 0.3m cable | 230.4K |
| PNP+JFET parasitic -12V | 230.4K |
| PNP external -5V | 460.8K |
| PNP+JFET external -5V | N/T |
| SN75150 | 921.6K |
| SN75C3232 | N/T |
| MAX3232 | N/T |
| MAX232 | N/T |
N/T – Not tested
6. Notes on driver selection
In this chapter I provide my motivation for driver selection.
I have looked for drivers in TI Interface Selection Guide. None of 1000 kbps drivers were available from local dealers (besides those drivers are not cheap). Therefore I decided to take a 120K driver and ‘overclock’ it. Considering that the current level is important for driving capacitive load, I limited my selection to dual supply chips. With these constraints I picked the smallest PDIP chip available locally and it happens to be SN75150. Its advantages: small footprint, very little overhead, level compatibility with PNP-based design, low price. Disadvantages ??“ necessity of dual power supply.
If dual power supply is not acceptable, you may try other drivers (such as SN75C3232, MAX3232, MAX232). I would appreciate if you share your results with me.
Post a Comment